Tuần tự hoá dữ liệu
Khi nói đến tuần tự hoá nghĩa là tác giả đang muốn đề cập đến cả tuần tự và phi tuần tự hoá dữ liệu.
Tuần tự hoá tham gia vào một vài điểm trong vòng đời của Solana Program và Program Account:
- Tuần tự hoá dữ liệu câu chỉ thị được gửi từ người dùng
- Phi tuần tự hoá dữ liệu chỉ thị trong Program
- Tuần tự hoá dữ liệu Account trong Program
- Phi tuần tự hoá dữ liệu Account ở phía người dùng
Một điều quan trọng là tất cả các quá trình bên trên đều được hỗ trợ bởi duy nhất một phương pháp tuần tự hoá. Một vài đoạn code mẫu trong bài sẽ sử dụng Borsh để làm ví dụ.
Phần còn lại sẽ được trích dẫn hầu hết từ Solana CLI Program Template.
Cài đặt Tuần tự hoá Borsh
Những thư viện lập trình cho Borsh phải được cài đặt tương thích với chương trình Rust, Node, và/hoặc Python.
[package]
name = "solana-cli-template-program-bpf"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2018"
license = "WTFPL"
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
[features]
no-entrypoint = []
[dependencies]
borsh = "0.9.0"
lazy_static = "1.4.0"
num-derive = "0.3"
num_enum = "0.5.1"
num-integer = "0.1.44"
num-traits = "0.2"
sol-template-shared = {path = "../shared"}
solana-program = "1.8.2"
thiserror = "1.0"
[dev-dependencies]
solana-program-test = "1.8.2"
solana-sdk = "1.8.2"
[lib]
crate-type = ["cdylib", "lib"]
[package]
name = "cli-program-template"
version = "0.1.5"
edition = "2018"
license = "WTFPL"
publish = false
[dependencies]
borsh = "0.9.0"
clap = "2.33.3"
lazy_static = "1.4.0"
serde = { version = "1.0.125", features = ["derive"] }
serde_yaml = "0.8.17"
sol-template-shared = {path = "shared"}
solana-clap-utils = "1.8.2"
solana-cli-config = "1.8.2"
solana-client = "1.8.2"
solana-logger = "1.8.2"
solana-remote-wallet = "1.8.2"
solana-sdk = "1.8.2"
tokio = { version = "1", features = ["full"] }
[workspace]
members = [
"program",
"shared",
]
[dev-dependencies]
lazy_static = "1.4.0"
solana-validator = "1.8.2"
solana-streamer = "1.8.2"
{
"name": "ts-program-template",
"version": "0.1.0",
"description": "Sample TS App",
"main": "client/nmain.ts",
"author": "",
"keywords": [],
"workspace": "client/",
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "https: //github.com/hashblock/solana-cli-program-template"
},
"homepage": "https: //github.com/hashblock/solana-cli-program-template",
"scripts": {
"test:all": "npm run build:client && npm run test:client",
"build:client": "rm -rf ./.dist/client && tsc ",
"start": "node ./node_modules/.bin/mocha .dist/client/main.js",
"test:client": "npm run start",
"lint": "eslint --ext .ts client/* && prettier --check \"client/**/*.ts\"",
"lint:fix": "eslint --ext .ts client/* --fix",
"pretty": "prettier --write '{,client/**/}*.ts'"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@tsconfig/recommended": "^1.0.1",
"@types/chai": "^4.3.0",
"@types/eslint": "^7.28.2",
"@types/eslint-plugin-prettier": "^3.1.0",
"@types/mkdirp": "^1.0.2",
"@types/mocha": "^9.0.0",
"@types/prettier": "^2.4.1",
"@typescript-eslint/eslint-plugin": "^5.6.0",
"@typescript-eslint/parser": "^5.6.0",
"chai": "^4.3.4",
"eslint": "^8.2.0",
"eslint-config-google": "^0.14.0",
"eslint-config-prettier": "^8.3.0",
"eslint-plugin-prettier": "^4.0.0",
"html-webpack-plugin": "^5.5.0",
"mocha": "^9.1.3",
"prettier": "^2.4.1",
"start-server-and-test": "^1.14.0",
"ts-node": "^10.4.0",
"typescript": "^4.5.2"
},
"dependencies": {
"@solana/web3.js": "^1.31.0",
"borsh": "^0.7.0",
"env": "^0.0.2",
"fs": "^0.0.1-security",
"mkdirp": "^1.0.4",
"npm-check-updates": "^12.0.3",
"sync-request": "^6.1.0",
"update": "^0.4.2"
}
}
borsh-construct==0.1.0
solana==0.20.0
Làm thế nào để tuần tự hoá dữ liệu của các chỉ thị từ phía người dùng
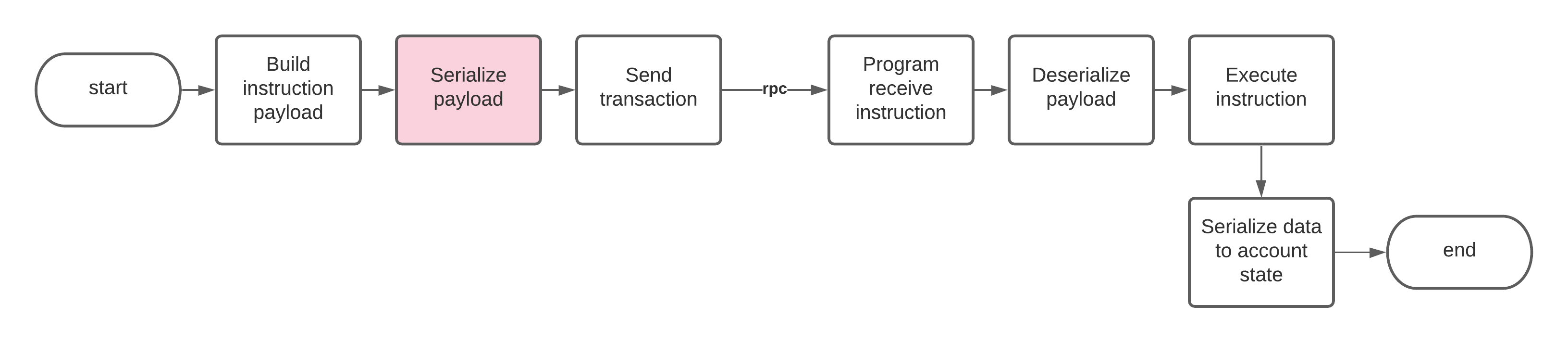
Nếu bạn đang tuần tự hoá dữ liệu của một chỉ thị ở phía người dùng để gửi lên Program, bạn cần chắc chắn rằng Program sẽ phi tuần tự hoá chỉ thị đó và đúng nguyên bản ban đầu.
Trong mẫu sau, một khối dữ liệu chỉ thị được chứa trong một mảng tuần tự như sau:
| Chỉ thị (Chỉ mục) | Khoá tuần tự | Giá trị tuần tự |
|---|---|---|
| Initialize (0) | Bất khả thi cho chỉ thị | Bất khả thi cho chỉ thị |
| Mint (1) | "foo" | "bar" |
| Transfer (2) | "foo" | Bất khả thi cho chỉ thị |
| Burn (3) | "foo" | Bất khả thi cho chỉ thị |
Trong ví dụ sau đây, giả sử Program sở hữu Account đã được khởi tạo từ trước.
// Include borsh functionality
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
// Get Solana
import {
Keypair,
Connection,
PublicKey,
Transaction,
TransactionInstruction,
sendAndConfirmTransaction,
} from "@solana/web3.js";
// Flexible class that takes properties and imbues them
// to the object instance
class Assignable {
constructor(properties) {
Object.keys(properties).map((key) => {
return (this[key] = properties[key]);
});
}
}
// Our instruction payload vocabulary
class Payload extends Assignable {}
// Borsh needs a schema describing the payload
const payloadSchema = new Map([
[
Payload,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["id", "u8"],
["key", "string"],
["value", "string"],
],
},
],
]);
// Instruction variant indexes
enum InstructionVariant {
InitializeAccount = 0,
MintKeypair,
TransferKeypair,
BurnKeypair,
}
/**
* Mint a key value pair to account
* @param {Connection} connection - Solana RPC connection
* @param {PublicKey} progId - Sample Program public key
* @param {PublicKey} account - Target program owned account for Mint
* @param {Keypair} wallet - Wallet for signing and payment
* @param {string} mintKey - The key being minted key
* @param {string} mintValue - The value being minted
* @return {Promise<Keypair>} - Keypair
*/
export async function mintKV(
connection: Connection,
progId: PublicKey,
account: PublicKey,
wallet: Keypair,
mintKey: string,
mintValue: string
): Promise<string> {
// Construct the payload
const mint = new Payload({
id: InstructionVariant.MintKeypair,
key: mintKey, // 'ts key'
value: mintValue, // 'ts first value'
});
// Serialize the payload
const mintSerBuf = Buffer.from(serialize(payloadSchema, mint));
// console.log(mintSerBuf)
// => <Buffer 01 06 00 00 00 74 73 20 6b 65 79 0e 00 00 00 74 73 20 66 69 72 73 74 20 76 61 6c 75 65>
// let mintPayloadCopy = deserialize(schema, Payload, mintSerBuf)
// console.log(mintPayloadCopy)
// => Payload { id: 1, key: 'ts key', value: 'ts first value' }
// Create Solana Instruction
const instruction = new TransactionInstruction({
data: mintSerBuf,
keys: [
{ pubkey: account, isSigner: false, isWritable: true },
{ pubkey: wallet.publicKey, isSigner: false, isWritable: false },
],
programId: progId,
});
// Send Solana Transaction
const transactionSignature = await sendAndConfirmTransaction(
connection,
new Transaction().add(instruction),
[wallet],
{
commitment: "singleGossip",
preflightCommitment: "singleGossip",
}
);
console.log("Signature = ", transactionSignature);
return transactionSignature;
}
from borsh_construct import String, CStruct, U8
from enum import IntEnum
from solana.rpc.types import RPCResponse
from solana.transaction import Transaction, TransactionInstruction, AccountMeta
from solana.publickey import PublicKey
from solana.keypair import Keypair
from solana.rpc.api import Client
# Instruction variants for target program
class InstructionVariant(IntEnum):
INITIALIZE = 0
MINT = 1
TRANSFER = 2
BURN = 3
# Schema for sending instructionVariants to on-chain sample program
payload_schema = CStruct("id" / U8, "key" / String, "value" / String)
def construct_payload(instruction_variant: InstructionVariant, key: str, value: str):
"""Generate a serialized instructionVariant"""
return payload_schema.build({"id": instruction_variant, "key": key, "value": value})
def mint_kv(
client: Client,
program_pk: PublicKey,
account_pk: PublicKey,
wallet_kp: Keypair,
mint_key: str,
mint_value: str,
) -> RPCResponse:
"""Mint with a key/value pair to an account"""
# Construct the program payload for Mint invariant
payload_ser = construct_payload(InstructionVariant.MINT, mint_key, mint_value)
# print(payload_ser)
# => b'\x01\n\x00\x00\x00python key\x0c\x00\x00\x00python value'
# mint_payload_copy = payload_schema.parse(payload_ser)
# print(mint_payload_copy)
# => Container:
# => initialized = 1
# => key = u'python key' (total 10)
# => value = u'python value' (total 12)
# Construct the transaction with instructionVariant
txn = Transaction().add(
TransactionInstruction(
[AccountMeta(account_pk, False, True)], program_pk, payload_ser
)
)
return client.send_transaction(txn, wallet_kp)
# => {'jsonrpc': '2.0', 'result': '4ZdpWNdovdVaLextWSiqEBWp67k9rNTTUaX3qviHDXWY9c98bVtaRt5sasPhYzMVXHqhex78gzNKytcBnVH5CSTZ', 'id': 2}
/// Instruction payload gets serialized
#[derive(BorshSerialize)]
pub struct Payload<'a> {
variant: u8,
key: &'a str,
value: &'a str,
}
/// Perform a mint transaction consisting of a key/value pair
/// See submit_transaction below
pub fn mint_transaction(
rpc_client: &RpcClient,
accounts: &[AccountMeta],
wallet_signer: &dyn Signer,
mint_key: &str,
mint_value: &str,
mint_instruction_id: u8,
commitment_config: CommitmentConfig,
) -> Result<Signature, Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
// Setup the payload. `mint_instruction_id` is instruction variant index = 1
let data = Payload<`_> {
variant: mint_instruction_id,
key: mint_key,
value: mint_value,
};
let instruction = Instruction::new_with_borsh(PROG_KEY.pubkey(), &data, accounts.to_vec());
submit_transaction(rpc_client, wallet_signer, instruction, commitment_config)
}
/// Submits the program instruction as per the
/// instruction definition
pub fn submit_transaction(
rpc_client: &RpcClient,
wallet_signer: &dyn Signer,
instruction: Instruction,
commitment_config: CommitmentConfig,
) -> Result<Signature, Box<dyn std::error::Error>> {
let mut transaction =
Transaction::new_unsigned(Message::new(&[instruction], Some(&wallet_signer.pubkey())));
let (recent_blockhash, _fee_calculator) = rpc_client
.get_recent_blockhash()
.map_err(|err| format!("error: unable to get recent blockhash: {}", err))?;
transaction
.try_sign(&vec![wallet_signer], recent_blockhash)
.map_err(|err| format!("error: failed to sign transaction: {}", err))?;
let signature = rpc_client
.send_and_confirm_transaction_with_spinner_and_commitment(&transaction, commitment_config)
.map_err(|err| format!("error: send transaction: {}", err))?;
Ok(signature)
}
Làm thế nào để phi tuần tự hoá dữ liệu của các chỉ thị trên Program
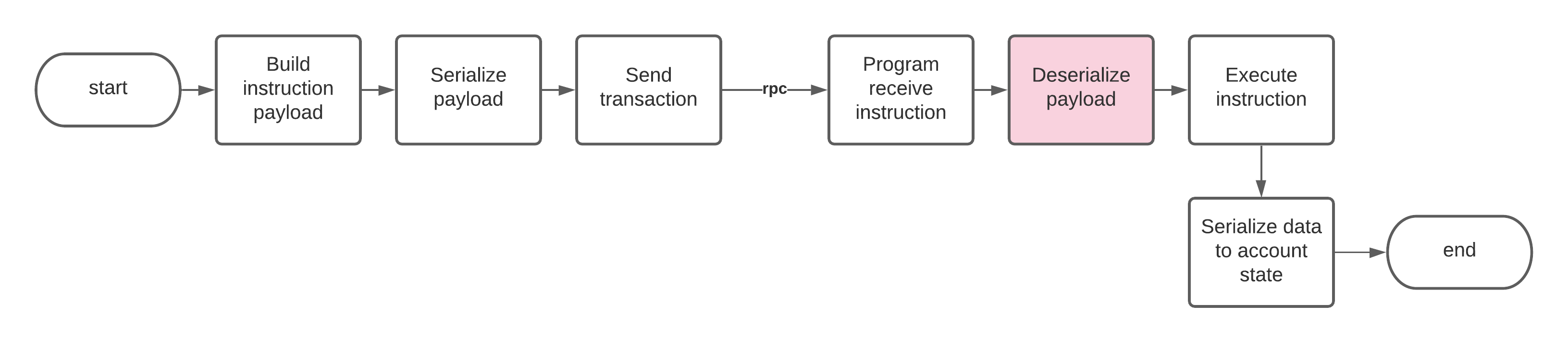
//! instruction Contains the main ProgramInstruction enum
use {
crate::error::SampleError, borsh::BorshDeserialize, solana_program::program_error::ProgramError,
};
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq)]
/// All custom program instructions
pub enum ProgramInstruction {
InitializeAccount,
MintToAccount { key: String, value: String },
TransferBetweenAccounts { key: String },
BurnFromAccount { key: String },
MintToAccountWithFee { key: String, value: String },
TransferBetweenAccountsWithFee { key: String },
BurnFromAccountWithFee { key: String },
}
/// Generic Payload Deserialization
#[derive(BorshDeserialize, Debug)]
struct Payload {
variant: u8,
arg1: String,
arg2: String,
}
impl ProgramInstruction {
/// Unpack inbound buffer to associated Instruction
/// The expected format for input is a Borsh serialized vector
pub fn unpack(input: &[u8]) -> Result<Self, ProgramError> {
let payload = Payload::try_from_slice(input).unwrap();
match payload.variant {
0 => Ok(ProgramInstruction::InitializeAccount),
1 => Ok(Self::MintToAccount {
key: payload.arg1,
value: payload.arg2,
}),
2 => Ok(Self::TransferBetweenAccounts { key: payload.arg1 }),
3 => Ok(Self::BurnFromAccount { key: payload.arg1 }),
4 => Ok(Self::MintToAccountWithFee {
key: payload.arg1,
value: payload.arg2,
}),
5 => Ok(Self::TransferBetweenAccountsWithFee { key: payload.arg1 }),
6 => Ok(Self::BurnFromAccountWithFee { key: payload.arg1 }),
_ => Err(SampleError::DeserializationFailure.into()),
}
}
}
Làm thế nào để tuần tự hoá dữ liệu Account trên Program
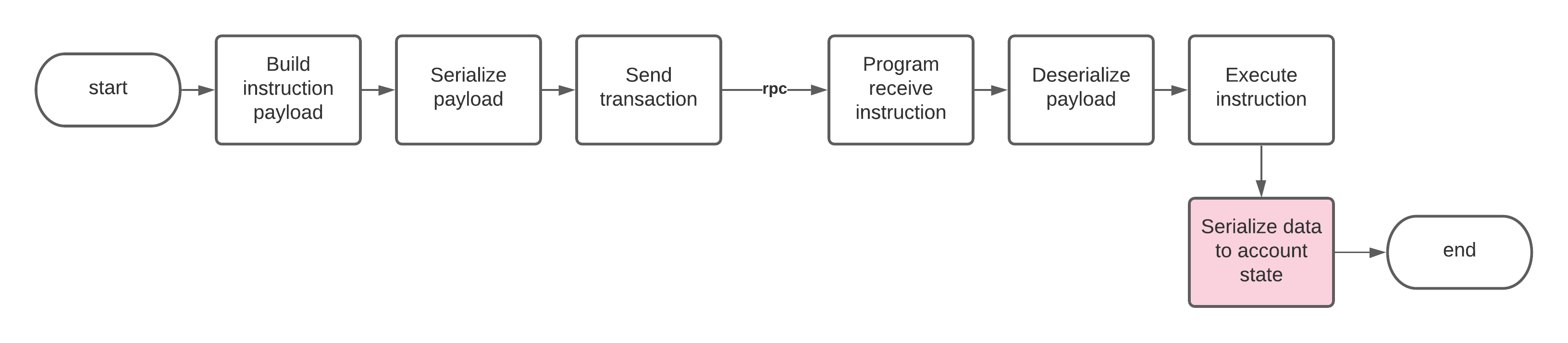
Một khối dữ liệu Account của Program (từ repo mẫu) được sắp xếp như sau:
| Byte 0 | Bytes 1-4 | Bytes còn lại (lên đến 1019) |
|---|---|---|
| Cờ khởi tạo | Độ dài của BTreeMap đã được tuần tự hoá | BTreeMap (nơi lưu trữ các cặp key-value) |
Pack (Đóng gói)
Từ Pack ở đây có nghĩa là một Trait (Đặc điểm) trong Rust.
Pack giúp quá trình tuần tự và phi tuần hoá ẩn đi những chi tiết phức tạp bên dưới, đồng thời cung cấp tính dễ đọc cho quá trình xử lý các chỉ thị trong Program. Thay vì đặt tất cả các đoạn mã tuần tự và phi tuần tự hoá trực tiếp trong quá trình xử lý của Program, chúng nên được trừu tượng hoá và đóng gói lại thành những hàm chức năng (3):
unpack_unchecked- Cho phép bạn phi tuần tự hoá dữ liệu Account mà không quan tấm Account đã khởi tạo hay chứa. Nó khá hữu ích khi bạn cần xử lý hàm Initialization (chỉ mục 0).unpack- Gọiunpack_from_slicetrong hiện thực Pack của bạn và kiểm tra xem Account đã được khởi tạo hay chưa.pack- Gọipack_into_slicetrong hiện thực Pack của bạn.
Dưới đây là một hiện thực Pack cho chương tình mẫu của chúng ta. Theo sau đó là đoạn code mẫu xử lý dữ liệu Account thực bằng Borsh.
//! @brief account_state manages account data
use crate::error::SampleError;
use sol_template_shared::ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE;
use solana_program::{
entrypoint::ProgramResult,
program_error::ProgramError,
program_pack::{IsInitialized, Pack, Sealed},
};
use std::collections::BTreeMap;
/// Maintains global accumulator
#[derive(Debug, Default, PartialEq)]
pub struct ProgramAccountState {
is_initialized: bool,
btree_storage: BTreeMap<String, String>,
}
impl ProgramAccountState {
/// Returns indicator if this account has been initialized
pub fn set_initialized(&mut self) {
self.is_initialized = true;
}
/// Adds a new key/value pair to the account
pub fn add(&mut self, key: String, value: String) -> ProgramResult {
match self.btree_storage.contains_key(&key) {
true => Err(SampleError::KeyAlreadyExists.into()),
false => {
self.btree_storage.insert(key, value);
Ok(())
}
}
}
/// Removes a key from account and returns the keys value
pub fn remove(&mut self, key: &str) -> Result<String, SampleError> {
match self.btree_storage.contains_key(key) {
true => Ok(self.btree_storage.remove(key).unwrap()),
false => Err(SampleError::KeyNotFoundInAccount),
}
}
}
impl Sealed for ProgramAccountState {}
// Pack expects the implementation to satisfy whether the
// account is initialzed.
impl IsInitialized for ProgramAccountState {
fn is_initialized(&self) -> bool {
self.is_initialized
}
}
impl Pack for ProgramAccountState {
const LEN: usize = ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE;
/// Store 'state' of account to its data area
fn pack_into_slice(&self, dst: &mut [u8]) {
sol_template_shared::pack_into_slice(self.is_initialized, &self.btree_storage, dst);
}
/// Retrieve 'state' of account from account data area
fn unpack_from_slice(src: &[u8]) -> Result<Self, ProgramError> {
match sol_template_shared::unpack_from_slice(src) {
Ok((is_initialized, btree_map)) => Ok(ProgramAccountState {
is_initialized,
btree_storage: btree_map,
}),
Err(_) => Err(ProgramError::InvalidAccountData),
}
}
}
Tuần tự hoá và Phi tuần tự hoá
Để hoàn thành các hàm tuần tự và phi tuần tự hoá cơ sở:
sol_template_shared::pack_into_slice- Điểm thực sự diễn ra quá trình tuần tự hoásol_template_shared::unpack_from_slice- Điểm thực sự diễn ra quá trình phi tuần tự hoá
Lưu ý rằng trong code mẫu bên dưới, chúng ta có một vùng nhớ 4 bytes cho u32 dành cho BTREE_LENGTH ngay trước BTREE_STORAGE. Việc này giúp Borsh, trong quá trình phi tuần tự hoá, có thể kiểm tra độ lớn của vùng nhớ mà nó cần phải trích xuất để xử lý, cũng như tái tạo lại đối tượng đã được tuần tự hoá trước đây. Phương pháp này được minh hoạ bên dưới khi mà BTREE_LENGTH được đọc trước tiên nhắm lấy được kích thước của slice ra khỏi con trỏ BTREE_STROAGE.
use {
arrayref::*,
borsh::{BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize},
solana_program::program_memory::sol_memcpy,
std::{collections::BTreeMap, error::Error},
};
/// Initialization flag size for account state
pub const INITIALIZED_BYTES: usize = 1;
/// Storage for the serialized size of the BTreeMap control
pub const BTREE_LENGTH: usize = 4;
/// Storage for the serialized BTreeMap container
pub const BTREE_STORAGE: usize = 1019;
/// Sum of all account state lengths
pub const ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE: usize = INITIALIZED_BYTES + BTREE_LENGTH + BTREE_STORAGE;
/// Packs the initialized flag and data content into destination slice
#[allow(clippy::ptr_offset_with_cast)]
pub fn pack_into_slice(
is_initialized: bool,
btree_storage: &BTreeMap<String, String>,
dst: &mut [u8],
) {
let dst = array_mut_ref![dst, 0, ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE];
// Setup pointers to key areas of account state data
let (is_initialized_dst, data_len_dst, data_dst) =
mut_array_refs![dst, INITIALIZED_BYTES, BTREE_LENGTH, BTREE_STORAGE];
// Set the initialized flag
is_initialized_dst[0] = is_initialized as u8;
// Store the core data length and serialized content
let keyval_store_data = btree_storage.try_to_vec().unwrap();
let data_len = keyval_store_data.len();
if data_len < BTREE_STORAGE {
data_len_dst[..].copy_from_slice(&(data_len as u32).to_le_bytes());
sol_memcpy(data_dst, &keyval_store_data, data_len);
} else {
panic!();
}
}
/// Unpacks the data from slice and return the initialized flag and data content
#[allow(clippy::ptr_offset_with_cast)]
pub fn unpack_from_slice(src: &[u8]) -> Result<(bool, BTreeMap<String, String>), Box<dyn Error>> {
let src = array_ref![src, 0, ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE];
// Setup pointers to key areas of account state data
let (is_initialized_src, data_len_src, data_src) =
array_refs![src, INITIALIZED_BYTES, BTREE_LENGTH, BTREE_STORAGE];
let is_initialized = match is_initialized_src {
[0] => false,
[1] => true,
_ => {
return Err(Box::<dyn Error>::from(format!(
"unrecognized initialization flag \"{:?}\". in account",
is_initialized_src
)))
}
};
// Get current size of content in data area
let data_len = u32::from_le_bytes(*data_len_src) as usize;
// If emptry, create a default
if data_len == 0 {
Ok((is_initialized, BTreeMap::<String, String>::new()))
} else {
let data_dser = BTreeMap::<String, String>::try_from_slice(&data_src[0..data_len]).unwrap();
Ok((is_initialized, data_dser))
}
}
Cách dùng
Sau đây, chúng ta sẽ tổng hợp lại tất cả các đoạn code mẫu bên trên và giải thích cách mà Program tương tác với ProgramAccountState. Trong đó, ProgramAccountState là đóng gói của trạng thái khởi tạo của Account cũng như BTreeMap cho các cặp key-value.
Đầu tiên, để khởi tạo một Account mới hoàn toàn:
/// Initialize a new program account, which is the first in AccountInfo array
fn initialize_account(accounts: &[AccountInfo]) -> ProgramResult {
msg!("Initialize account");
let account_info_iter = &mut accounts.iter();
let program_account = next_account_info(account_info_iter)?;
let mut account_data = program_account.data.borrow_mut();
// Here we use unpack_unchecked as we have yet to initialize
// Had we tried to use unpack it would fail because, well, chicken and egg
let mut account_state = ProgramAccountState::unpack_unchecked(&account_data)?;
// We double check that we haven't already initialized this accounts data
// more than once. If we are good, we set the initialized flag
if account_state.is_initialized() {
return Err(SampleError::AlreadyInitializedState.into());
} else {
account_state.set_initialized();
}
// Finally, we store back to the accounts space
ProgramAccountState::pack(account_state, &mut account_data).unwrap();
Ok(())
}
Sau đó, chúng ta có thể dùng chúng trong quá trình xử lý của các chỉ thị. Ví như minh hoạ bên dưới có thể tiếp nhận chỉ thị từ phía người dùng và gán một cặp key-value vào trong ProgramAccountState đã khởi tạo bên trên.
/// Mint a key/pair to the programs account, which is the first in accounts
fn mint_keypair_to_account(accounts: &[AccountInfo], key: String, value: String) -> ProgramResult {
msg!("Mint to account");
let account_info_iter = &mut accounts.iter();
let program_account = next_account_info(account_info_iter)?;
let mut account_data = program_account.data.borrow_mut();
// Unpacking an uninitialized account state will fail
let mut account_state = ProgramAccountState::unpack(&account_data)?;
// Add the key value pair to the underlying BTreeMap
account_state.add(key, value)?;
// Finally, serialize back to the accounts data
ProgramAccountState::pack(account_state, &mut account_data)?;
Ok(())
}
Làm thế nào để tuần hoá dữ liệu Account ở phía người dùng
Người dùng có thể gọi Solana để lấy dữ liệu dưới dạng các khối dữ liệu đã được tuần tự hoá. Quá trình phi tuần tự hoá dữ liệu này cần người dùng phải hiểu được cấu trúc của dữ liệu gốc.
Cấu trúc của dữ liệu Account được định nghĩa ở đây
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import {
Keypair,
AccountMeta,
Connection,
LAMPORTS_PER_SOL,
PublicKey,
SystemProgram,
Transaction,
TransactionInstruction,
sendAndConfirmTransaction,
} from "@solana/web3.js";
// Flexible class that takes properties and imbues them
// to the object instance
class Assignable {
constructor(properties) {
Object.keys(properties).map((key) => {
return (this[key] = properties[key]);
});
}
}
export class AccoundData extends Assignable {}
const dataSchema = new Map([
[
AccoundData,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["initialized", "u8"],
["tree_length", "u32"],
["map", { kind: "map", key: "string", value: "string" }],
],
},
],
]);
/**
* Fetch program account data
* @param {Connection} connection - Solana RPC connection
* @param {PublicKey} account - Public key for account whose data we want
* @return {Promise<AccoundData>} - Keypair
*/
export async function getAccountData(
connection: Connection,
account: PublicKey
): Promise<AccoundData> {
let nameAccount = await connection.getAccountInfo(account, "processed");
return deserializeUnchecked(dataSchema, AccoundData, nameAccount.data);
}
import base64
from borsh_construct import CStruct, U8, U32, HashMap, String
from solana.rpc.commitment import Confirmed
from solana.publickey import PublicKey
from solana.rpc.api import Client
# Schema to deserialize program's account data
account_schema = CStruct(
"initialized" / U8,
"map_length" / U32,
"map" / HashMap(String, String)
)
def get_account_info(client: Client, account_pk: PublicKey):
"""Fetch account information from RPC, parse out the data and deserialize"""
res = client.get_account_info(account_pk, Confirmed, encoding='base64')
data = res['result']
if isinstance(data, dict):
return account_schema.parse(base64.urlsafe_b64decode(data['value']['data'][0]))
else:
raise AttributeError(f'Unknown RPC result {data}')
# Results in or similar
# => Container:
# => initialized = 1
# => map_length = 109
# => map = {'Happy': 'New Year!', 'newKey': 'A new value',
# => 'python key': 'python value', 'ts key': 'ts first value'}
use {
arrayref::*,
borsh::{BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize},
std::{collections::BTreeMap, error::Error},
};
#[allow(clippy::ptr_offset_with_cast)]
pub fn unpack_from_slice(src: &[u8]) -> Result<(bool, BTreeMap<String, String>), Box<dyn Error>> {
let src = array_ref![src, 0, ACCOUNT_STATE_SPACE];
// Setup pointers to key areas of account state data
let (is_initialized_src, data_len_src, data_src) =
array_refs![src, INITIALIZED_BYTES, BTREE_LENGTH, BTREE_STORAGE];
let is_initialized = match is_initialized_src {
[0] => false,
[1] => true,
_ => {
return Err(Box::<dyn Error>::from(format!(
"unrecognized initialization flag \"{:?}\". in account",
is_initialized_src
)))
}
};
// Get current size of content in data area
let data_len = u32::from_le_bytes(*data_len_src) as usize;
// If emptry, create a default
if data_len == 0 {
Ok((is_initialized, BTreeMap::<String, String>::new()))
} else {
let data_dser = BTreeMap::<String, String>::try_from_slice(&data_src[0..data_len]).unwrap();
Ok((is_initialized, data_dser))
}
}
Mapping cơ bản bằng TS/JS cho Solana
Mô tả của Borsh chứa hầu hết các mapping cho các dữ liệu nguyên thuỷ và các dữ liệu phức.
Mấu chốt trong TS/JS, và kể cả Python, là tạo ra một Borsh Schema với các định nghĩa chính xác sao cho việc tuần tự và phi tuần tuận hoá có thể vận hành được trên dữ liệu đầu vào.
Sau đây là một minh hoạ về tuần tự hoá dữ liệu nguyên thuỷ (numbers, strings) và dữ liệu phức (array với kích thức cố định, Map) trong Typescript hoặc Python. Tiếp đến là phi tuần tự hoá dữ liệu đó bằng Rust.
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import { expect } from "chai";
import { PublicKey, Struct } from "@solana/web3.js";
/**
* Primitive extends the Struct type from Solana Library
* for convenience of dynamic property setting
* @extends {Struct} Solana JS Struct class
*/
class Primitive extends Struct {
constructor(properties) {
super(properties);
}
}
/**
* Entry point for script *
*/
async function entry() {
// Emulate BTreeMap
let map = new Map();
map.set("cookbook", "recipe");
map.set("recipe", "ingredient");
// Setup a Primitive for all basic and a few
// compound types
const value = new Primitive({
U8: 255,
U16: 65535,
U32: 4294967295,
FIXED_STRING_ARRAY: ["hello", "world"],
FIXED_U8_ARRAY: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
MAP_STRING_STRING: map,
});
// Define our schema
const schema = new Map([
[
Primitive,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["U8", "u8"],
["U16", "u16"],
["U32", "u32"],
["FIXED_STRING_ARRAY", ["string", 2]],
["FIXED_U8_ARRAY", ["u8", 5]],
[
"MAP_STRING_STRING",
{ kind: "map", key: "string", value: "string" },
],
],
},
],
]);
console.log("Value = ", value);
// Serialize then deserialize
const dser = Buffer.from(serialize(schema, value));
console.log(dser);
const newValue = deserialize(schema, Primitive, dser);
// Viola!
console.log("New value = ", newValue);
console.log("Fixed string array = ", newValue["FIXED_STRING_ARRAY"]);
console.log("Fixed u8 array = ", newValue["FIXED_U8_ARRAY"]);
console.log("Map = ", newValue["MAP_STRING_STRING"]);
}
entry();
import base64
from borsh_construct import U8, U16, U32, String, HashMap
# Schema to deserialize various types
primitive_schema = CStruct(
"U8" / U8,
"U16" / U16,
"U32" / U32,
"FIXED_STRING_ARRAY" / String[2],
"FIXED_U8_ARRAY" / U8[5],
"MAP_STRING_STRING" / HashMap(String, String)
)
def common():
mapping = {"cookbook": "recipe", "recipe": "ingredient"}
# Serialize
dser = primitive_schema.build({
'U8': 255,
'U16': 65535,
'U32': 4294967295,
"FIXED_STRING_ARRAY": ['hello', 'world'],
"FIXED_U8_ARRAY": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5],
"MAP_STRING_STRING": mapping})
print(dser)
# => b'\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\xff\x05\x00\x00\x00hello\x05\x00\x00\x00world\x01\x02\x03\x04\x05\x02\x00\x00\x00\x08\x00\x00\x00cookbook\x06\x00\x00\x00recipe\x06\x00\x00\x00recipe\n\x00\x00\x00ingredient'
# Deserialize
new_value = primitive_schema.parse(dser)
# Viola
print(new_value)
# => Container:
# => U8 = 255
# => U16 = 65535
# => U32 = 4294967295
# => FIXED_STRING_ARRAY = ListContainer:
# => hello
# => world
# => FIXED_U8_ARRAY = ListContainer:
# => 1
# => 2
# => 3
# => 4
# => 5
# => MAP_STRING_STRING = {'cookbook': 'recipe', 'recipe': 'ingredient'}
fn main() {}
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use borsh::{BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize};
use std::collections::BTreeMap;
#[test]
fn primitives() {
let prim = [
255u8, 255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 255, 5, 0, 0, 0, 104, 101, 108, 108, 111, 5, 0, 0, 0,
119, 111, 114, 108, 100, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 2, 0, 0, 0, 8, 0, 0, 0, 99, 111, 111, 107, 98,
111, 111, 107, 6, 0, 0, 0, 114, 101, 99, 105, 112, 101, 6, 0, 0, 0, 114, 101, 99, 105,
112, 101, 10, 0, 0, 0, 105, 110, 103, 114, 101, 100, 105, 101, 110, 116,
];
#[derive(BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize, Debug)]
struct Primitive(
u8,
u16,
u32,
String,
String,
[u8; 5],
BTreeMap<String, String>,
);
let x = Primitive::try_from_slice(&prim).unwrap();
println!("{:?}", x);
}
}
Kiểu dữ liệu nâng cao
Chúng ta đã đi qua nội dung cơ bản ở các ví dụ trước. Nhưng ngoài ra, Solana còn có một vài kiểu dự liệu tự định nghĩa khác. Trong phần này, chúng ta tìm hiểu qua các xử lý chúng bằng TS/JS và Rust.
COption
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { serialize, deserialize, deserializeUnchecked } from "borsh";
import { Buffer } from "buffer";
import { PublicKey, Struct } from "@solana/web3.js";
/**
* COption is meant to mirror the
* `solana_program::options::COption`
*
* This type stores a u32 flag (0 | 1) indicating
* the presence or not of a underlying PublicKey
*
* Similar to a Rust Option
* @extends {Struct} Solana JS Struct class
* @implements {encode}
*/
class COption extends Struct {
constructor(properties) {
super(properties);
}
/**
* Creates a COption from a PublicKey
* @param {PublicKey?} akey
* @returns {COption} COption
*/
static fromPublicKey(akey?: PublicKey): COption {
if (akey == undefined) {
return new COption({
noneOrSome: 0,
pubKeyBuffer: new Uint8Array(32),
});
} else {
return new COption({
noneOrSome: 1,
pubKeyBuffer: akey.toBytes(),
});
}
}
/**
* @returns {Buffer} Serialized COption (this)
*/
encode(): Buffer {
return Buffer.from(serialize(COPTIONSCHEMA, this));
}
/**
* Safe deserializes a borsh serialized buffer to a COption
* @param {Buffer} data - Buffer containing borsh serialized data
* @returns {COption} COption object
*/
static decode(data): COption {
return deserialize(COPTIONSCHEMA, this, data);
}
/**
* Unsafe deserializes a borsh serialized buffer to a COption
* @param {Buffer} data - Buffer containing borsh serialized data
* @returns {COption} COption object
*/
static decodeUnchecked(data): COption {
return deserializeUnchecked(COPTIONSCHEMA, this, data);
}
}
/**
* Defines the layout of the COption object
* for serializing/deserializing
* @type {Map}
*/
const COPTIONSCHEMA = new Map([
[
COption,
{
kind: "struct",
fields: [
["noneOrSome", "u32"],
["pubKeyBuffer", [32]],
],
},
],
]);
/**
* Entry point for script *
*/
async function entry(indata?: PublicKey) {
// If we get a PublicKey
if (indata) {
// Construct COption instance
const coption = COption.fromPublicKey(indata);
console.log("Testing COption with " + indata.toBase58());
// Serialize it
let copt_ser = coption.encode();
console.log("copt_ser ", copt_ser);
// Deserialize it
const tdone = COption.decode(copt_ser);
console.log(tdone);
// Validate contains PublicKey
if (tdone["noneOrSome"] == 1) {
console.log("pubkey: " + new PublicKey(tdone["pubKeyBuffer"]).toBase58());
}
/*
Output:
Testing COption with A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU
copt_ser Buffer(36) [1, 0, 0, 0, 135, 202, 71, 214, 68, 105, 98, 176, 211, 130, 105, 2, 55, 187, 86, 186, 109, 176, 80, 208, 77, 100, 221, 101, 20, 203, 149, 166, 96, 171, 119, 35, buffer: ArrayBuffer(8192), byteLength: 36, byteOffset: 1064, length: 36]
COption {noneOrSome: 1, pubKeyBuffer: Uint8Array(32)}
pubkey: A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU
*/
} else {
console.log("Testing COption with null");
// Construct COption instance
const coption = COption.fromPublicKey();
// Serialize it
const copt_ser = coption.encode();
console.log(copt_ser);
// Deserialize it
const tdone1 = COption.decode(copt_ser);
console.log(tdone1);
// Validate does NOT contains PublicKey
if (tdone1["noneOrSome"] == 1) {
throw Error("Expected no public key");
} else console.log("pubkey: null");
/*
Output:
Testing COption with null
Buffer(36)[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, buffer: ArrayBuffer(8192), byteLength: 36, byteOffset: 2272, length: 36]
COption { noneOrSome: 0, pubKeyBuffer: Uint8Array(32) }
pubkey: null
*/
}
}
// Test with PublicKey
entry(new PublicKey("A94wMjV54C8f8wn7zL8TxNCdNiGoq7XSN7vWGrtd4vwU"));
console.log("");
// Test without PublicKey
entry();
fn main() {}
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
use arrayref::{array_ref, array_refs};
use solana_program::{program_option::COption, pubkey::Pubkey};
/// Emulate how COption is 'unpacked'
fn deser_option(data: &[u8]) -> COption<Pubkey> {
// Map the data block
let ain = array_ref![data, 0, 36];
let (base, key) = array_refs![ain, 4, 32];
// Get the SOME or NONE u32
let nos = u32::from_le_bytes(*base);
// Construct the COption accordingly
let opt: COption<Pubkey> = if nos == 0 {
COption::None
} else {
COption::Some(Pubkey::new_from_array(*key))
};
opt
}
#[test]
fn btest() {
// From Typescript with borsh'ing
let copt = [
1u8, 0, 0, 0, 135, 202, 71, 214, 68, 105, 98, 176, 211, 130, 105, 2, 55, 187, 86, 186,
109, 176, 80, 208, 77, 100, 221, 101, 20, 203, 149, 166, 96, 171, 119, 35,
];
// Emulate COption deserialization
let coption = deser_option(&copt);
if coption.is_some() {
println!("{:?}", coption.expect("Uh-oh"));
}
// As a Borsh Struct
#[derive(BorshDeserialize, BorshSerialize, Debug)]
struct TOption(u32, [u8; 32]);
let toption = TOption::try_from_slice(&copt).unwrap();
let pkey = Pubkey::new_from_array(toption.1);
println!("Some = {:?} Pubkey = {:?}", toption.0, pkey);
}
}